 Schematic illustration
Schematic illustrationAbstract
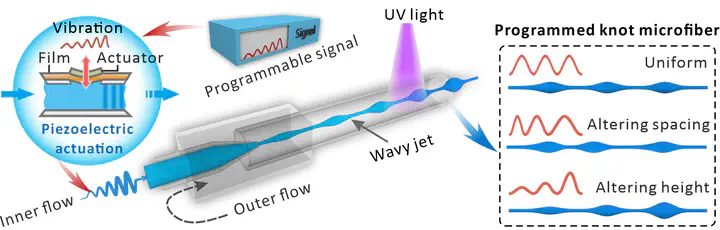
Microfibers have demonstrated significant application values in a large number of areas. Current efforts focus on developing new technologies toprepare microfibers with controllable morphological and structural features to enhance their functions. Here, a piezoelectric microfluidic platform ispresented for consecutive spinning of functional microfibers with programmable spindle-knots. In this platform, a jet of a pregel-solution flowing in thechannel can be subjected to a programmable piezoelectric signal and vibrates synchronously. Following a rapid polymerization of the wavy jet, microfiberswith corresponding morphologies can be generated, including uniform, gradient, and symmetrical knots. Such a unique knot structure contributes to awater-collection mechanism. Thus, it has been observed that microfibers with programmed knots enable even more flexible droplet handling and activewater transport. In addition, by constructing higher-order knot fiber networks, practical applications including spray reaction, lab-on-a-chip vapor detection,etc., can also be demonstrated. it is believed that this platform opens a new avenue for fiber spinning, and the programmable microfibers would be highlyapplicable in chemical, biomedical, and environmental areas.